英國dissertation范文:品牌管理中的品牌歷史概念的意義

09-15, 2017
我提出我的論點來證明一個品牌實際上需要一個歷史在當今動態(tài)的情況下取得成功并長期生存下去。
首先我要給工作的基本定義,試圖從理論的角度界定品牌的歷史;然后我要分析這些理論的影響為了維持我的論點;最后我要在當今市場,用現(xiàn)實的案例給出建議,得出自己的結(jié)論。
要確定一個品牌是否需要一個歷史作為一個資產(chǎn),重要的是要確定工作的關(guān)鍵要素。
品牌的定義是一個很好的起點,因為這個詞本身可以被提到許多不同的主題和意義。這將有助于限制研究領(lǐng)域。
1. INTRODUCTION 簡介
I'm presenting my arguments to prove that a brand actually need a history to be successful in nowadays dynamic scenario and to survive in the long term.
First I'm going to give basic definitions to work on, trying to define brand history by a theoretical point of view; then I'm going to analyze those theories implications in order to sustain my arguments; finally I'm going to use real-life cases in nowadays market to give recommendations and draw my conclusions.
2. DEFINITIONS TO START 定義
To determine whether or not a brand needs a history as an asset, is important to identify the key elements to work on.
A definition of brand is a good starting point, since the word itself could be referred to many different themes and meanings. This will surely help to restrict the field of study.
For Gardner and Levy's (1955) "A brand name is more than the label employed to differentiate among the manufacturers of a product; It is a complex symbol that represents a variety of ideas and attributes. It tells the consumers many thing, not only by the way it sounds (and the literal meaning if it has one) but, more important, via the body of associations it has built up and acquired as a public object over a period of time."
Following this logic the brand could also be conceptualized as a bundle of tangible and intangible features which increase the attractiveness of a product beyond its functional value (Farquhar, 1989; Park and Srinivasan, 1994).
History in this case could play a crucial role in binding tangible and intangible features by using a "continuous chronological record of important events"(Oxford Dictionaries) allowing a brand or a company, to recall a complex set of meanings, values and symbols connected to origins, past performances and mythologized episodes.
This process of recalling the past could be beneficial for both firm perspective and consumer perspective and it's connected to the concept of Brand Heritage.#p#分頁標題#e#
3. BRAND HISTORY AND BRAND HERITAGE 品牌歷史與品牌遺產(chǎn)
The word heritage is generally associated with inheritance: something transferred from one generation to another. As a concept, therefore, it works as a carrier of historical values from the past (Nuryanti, 1996).
On the surface the difference between heritage and history may seem minor. However, if history may explore and explain a past that is far away, heritage clarifies and makes that same past relevant for contemporary contexts and purposes.
In the present time characterized by high dynamics, uncertainty, and massive consumer disorientation , customers tend to prefer brands with a heritage: a brand infused with a heritage stands for authenticity, credibility, and trust, and can provide leverage for a brand, especially in global markets (Aaker 1996; George 2004).
The brand heritage construct can therefore be defined as " (…) a dimension of a brand's identity found in its track record, longevity, core values, use of symbols and particularly in an organisational belief that its history is important " (Urde et al. 2007). Based on the definition of brand heritage and its distinction from related constructs, it is useful to consider five major elements that indicate whether and to what extent heritage is present or potentially found in a brand (Urde, Greyser, and Balmer 2007, p. 9).
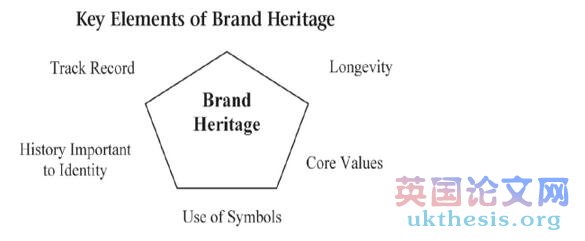
The element track record is related to the established performance that the brand or the company has been connected with, such as certain values and promises over time (Urde 1997).
The second element of brand heritage, longevity, is of special importance for large multigenerational family-owned companies reflecting sustainability and consistency (Urde, Greyser, and Balmer 2007, p. 9).
Core values encompass the basic values the brand is associated with. Like a promise or covenant in external communication, these values underline and help to define corporate strategy and are an integral part of the brand identity (Kapferer 2004; Lencioni 2002; Urde 1994).
The use of symbols is related to logos or designs and illustrates the brand's core meaning and ideas (Urde, Greyser, and Balmer 2007, p. 10).
The fifth component asks whether history is important to identity. Companies have to sense their own history as being crucially important to their identity. It is absolutely essential that they know who and what they are. This understanding should also be a key part of communication, advertising, and the marketing mix (Brown, Kozinets, and Sherry 2003b).
3.1 TYPE OF HERITAGE
#p#分頁標題#e#
Referring to the work of the sociologist George Herbert Mead about the impact of past on individuals understanding of reality, and following the research of Bradford T. Hudson and John M.T. Balmer (2013) it's possible to distinct between four different forms of Heritage.
Structural heritage
The nature of the present depends on the outcome of events that occurred in the past, which cannot be altered. Structural heritage involves a succession of causation from past to present.
*Brands that use structural heritage claim superiority and differentiation referring to a pedigree connecting the current company to the moment of origination and the people instrumental in establishing the company. Practical examples of structural heritage abound within many industries and sectors. For instance, some companies refer to founding dates
Implied heritage
If a company is vibrant and respected in the present, then it must have existed and developed during the past in a manner that explains its current status. Heritage is expressed by displaying current attributes that imply historical antecedents, by demonstrating congruence between current attributes and historical attributes, or by describing patterns of accomplishment across time. This dimension may also be indicated by references to the age of a brand.
*Claims of differentiation or superiority by the firm are validated through statements of longevity, or demonstrations of continuity between past and present.
Reconstructed heritage
This dimension suggests that our relationship to the past is interpretive and our understanding of prior events is enhanced through contemplation.
*Claims of differentiation or superiority by the firm are validated by the familiar or reminiscent character of the brand or its associated products. A commonly cited example of reconstructed heritage is the new Volkswagen Beetle, which was introduced in 1998 with design elements reminiscent of the original Beetle that became a cultural icon during the 1960s.
Mythical heritage
Mythical heritage refers to pasts that are partly or wholly fictitious, and which facilitate the projection or escape of consumers into imaginary worlds that relate to the brand. Mythical heritage is often expressed through fantasy or illusion, especially within communications narratives or the design of environments and products.
*Claims of differentiation or superiority by the firm are validated by the archetypal, universal or quintessential nature of brand attributes.
The reason companies with heritage should use it, is to take advantage of differentiation that is valuable for the customer/consumer and other stakeholders, distinctive for the brand, and difficult to imitate for the competitors. Heritage can provide a basis for distinctiveness in positioning, which can generate competitive advantage, e.g. translating into higher prices and margins, and retaining customers to whom heritage is meaningful.#p#分頁標題#e#
3.2 BRAND HERITAGE AND EFFECTS ON CUSTOMER VALUE
A brand with a heritage creates and confirms expectations about future behavior to stakeholder groups and makes a promise that the brand will continue to deliver on these commitments (e.g., Aaker 1996 ; George 2004 ). For this reason brand history along with brand heritage can add consumer perceived value and can minimize consumers' buying risk (Muehling and Sprott 2004 ).
For the conceptualization of consumer value we refer to four major types of customer perceived value:
1) Economic value:
The economic dimension of customer value addresses direct monetary aspects such as price, resale price, discount, investment etc. It refers to the value of the product expressed in dollars and cents, to what is given up or sacrificed to obtain a product (e.g., Ahtola 1984 ; Chapman 1986 ; Mazumdar 1986 ; Monroe and Krishnan 1985 ).
Functional value:
The functional dimension of customer value represents the core benefit and basic utilities such as e.g. the quality, the uniqueness, the usability, the reliability, and durability of a certain product (Sheth et al. 1991 ).
Affective value:
The affective dimension of customer value refers to the experiences, feelings, and emotions a certain brand or product provides to the consumer in addition to its functional utility (Hirschman and Holbrook 1982 ; Sheth et al. 1991 , Westbrook and Oliver 1991 ).
Social value:
The social dimension of customer value focuses a customer's personal orientation towards a brand or product and addresses personal matters such as consumer's self-concepts, self-worth or self-identity value (e.g., Vigneron and Johnson 2004 ; Hirschman and Holbrook 1982 ).
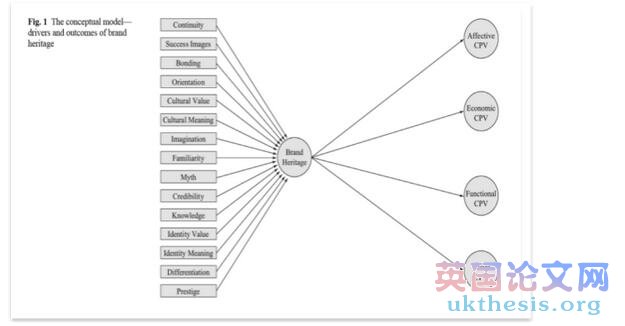
Following the study and the complex empirical research of Thomas Wuestefeld et al(2012) in the article " The impact of brand heritage on customer perceived value" we can say that brand heritage construct (as a result of different factors like history, prestige, longevity, myth and credibility) overall affects Consumer Perceived Value (CPV), therefore could be a crucial asset to consider.
4.EXAMPLES OF BRAND USING HERITAGE AS A COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE 以遺產(chǎn)為競爭優(yōu)勢的品牌實例
Tangible examples of a proper use of brand history and brand heritage could be seen in both luxury market and mass market.
4.1 KRAFT/CADBURYS ACQUISITION CASE STUDY
"A sophisticated understanding of the past is one of the most powerful tools we have for shaping the future".#p#分頁標題#e#
An actual implementation of brand history and brand heritage concepts could be seen in how Kraft Foods managed its 2010 integration of the British confectioner Cadbury. Cadbury's management and its employees had somehow mounted resistance to the acquisition, fearing the loss of core values and a products quality. To help smooth the process, senior executives turned to Kraft's long-established archives. Company archivists launched an intranet site, titled "Coming Together," that honored the parallel paths Kraft and Cadbury had taken. Poring over historical materials, they had found much evidence of shared values, and the presentation reinforced those common themes. In addition to the founders' stories, the intranet site included interactive time lines, iconic advertising images, brief documentary videos, and dozens of detailed histories of owned branded products all designed to show how leading Kraft and Cadbury brands had come to sit side by side on grocers' shelves. The same narrative took hold in other communications, from CEO speeches to press releases, and in employee training sessions. Kraft ended up integrating Cadbury more smoothly than any of its previous acquisitions. The history of the enterprise can instill a sense of identity and purpose and suggest the goals that will resonate (George Smith,Your Company's History as a Leadership Tool).
4.2 COCA-COLA is really proud of its history
"The Coca-Cola story is a good one, even if we do say so ourselves"
Coca-Cola, one of the most famous and iconic brand in the world definitely recurs to an implementation of brand heritage tools by referring to the company glorious longevity and past performances in a nostalgic fashion. An example of this commitment to history could definitely be found on Coca-Cola website with many pages dedicated to the evolution of the brand itself. A pdf for the 125 years anniversary of Coca-Cola has been released, with lot of documents and pictures of logos, packaging and successful advertising during the ages. A relevant proof of appliance of brand heritage construct in Coca-Cola marketing mix, could be found in the smart use of symbols (the iconic bottle and the famous Coca-Cola font) and the reiteration of the affective value(being on the market for such a long time it bears nostalgic potential for every adult consumer).
4.3 LOUIS VUITTON-The iconic traveling luggage
Louis Vuitton is a well known apparel luxury brand. It puts great emphasys on tradition as seen in the brand website rich in contents like old pictures and all sort of informations on the origins of the company itself. The starting point, the making of the iconic Louis Vuitton traveling luggage is used as tool of reference to the glorious past of the company itself and could be read as a clear example of reconstructed heritage. And plus, the promise of value connected to the purchase of those bags implies an increase of social perceived value for consumers as a form of self-actualization and distinction.#p#分頁標題#e#
4.4 BURBERRY-The invention of gabardine and the "myth" of the trench coat
Burberry is another famous luxury fashion brand which use history, tradition and heritage as crucial assets in its marketing mix .Its main fashion house focuses on outerwear, fashion accessories, fragrances, sunglasses, and cosmetics.
Established in 1856 by Thomas Burberry and originally focusing on the development of outdoor attire, the fashion house has moved on to the high fashion market developing pattern-based scarves, trench coats, and other fashion accessories. Its distinctive check pattern has become one of its most widely copied trademarks. The brand itself can count on the innovative invention of gabardine, a breathable and waterproof fabric which somehow revolutionized rainwear. Burberry is most famous for its trench coat. Its coats were worn in the trenches of World War I by British soldiers, and for decades thereafter Burberry became so much a part of British culture that Queen Elizabeth II and the Prince of Wales have granted the company Royal Warrants.
Thus, Burberry is the perfect example of a Heritage brand based on the implied heritage category: the respectability and the glorious status showed in the present is the result of a great and honorable past (invention of gabardine + fact that trench coats were used during world war)
5. CONCLUSION 結(jié)論
If lots of nowadays most successful brands are connected to the ever-innovating technology sector (think of Google, Apple, Amazon, Facebook etc) and don't rely too much on a long or mythicized history, long-standing brands combining both heritage and longevity are still able to deliver real value attaining strong competitive positions.
If we observe the 2016 Global Best Brands report by Interbrand, we can see that 10 brands in the top15 are more than 50 years old and some of them are way older than that. Even if someone could argue that the success of a brand has little to do with a brand's age, we can still say that having long-term traditions and experiences in the business could help to stay relevant and competitive.
The level of sophistication needed for a brand to maintain its competitive advantages is of course not to be underestimated, newness and innovation plays a strong role. "But even if a brand needs to evolve constantly to stay relevant, it also needs a center of gravity, a clear vision and a commitment to stay true to the core of its DNA" (Rebecca Robins 2015)
In conclusion we can say that:
Consumers prefer brands with a history in order to be reassured and to fight purchasing uncertainty
Brand History is a key element in the implementation of Brand Heritage constructïƒ Brand Heritage boost the Consumer Perceived Value#p#分頁標題#e#
A connection to the past is often required by a company to be successful and coherent in the present and to grow in the future.
