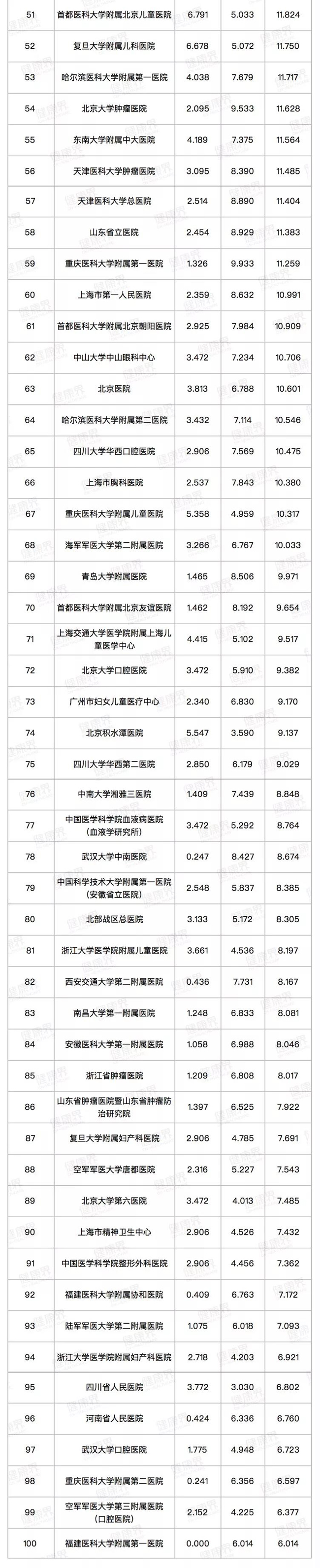
2019年11月10日,復旦大學醫院管理研究所發布“復旦版中國醫院排行榜”。


2019-11-12 海扶醫療
2019年11月10日,復旦大學醫院管理研究所發布“復旦版中國醫院排行榜”。


重慶健康產業“十四五”規劃明確提出做強海扶刀?等標志性品牌產品成果
近日,重慶市人民政府辦公廳發布《關于印發重慶市大健康產業發展“十四五”規劃(2021—2025年)的通知》(渝府辦發〔2021〕155號,以下簡稱《規劃》)。

祝賀長沙市婦幼保健院裝機首年手術量創全球第一
長沙市婦幼保健院于2020年12月引進全新一代海扶刀?聚焦超聲腫瘤治療系統(JC200D1),建立海扶?微無創治療中心,裝機首年完成551臺聚焦超聲消融手術,創全球第一

中南大學湘雅三醫院已成功完成超7000例子宮、良惡性疾病的聚焦超聲消融治療
截至2021年11月,中南大學湘雅三醫院已成功完成超7000例子宮良惡性疾病的聚焦超聲消融治療,造福了省內外無數廣大婦女患者。
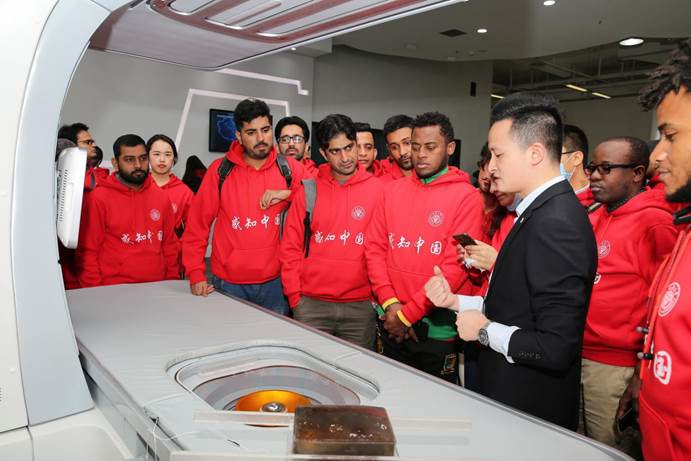

感知海扶,領跑超聲無創
2021年10月22日,由國家留學基金委主辦,重慶大學承辦的“感知中國—智造重慶”主題文化實踐活動代表團一行,來自巴基斯坦、也門、埃塞俄比亞、玻利維亞等20個國家的39名留學生們走進海扶醫療感受聚焦超聲治療領域的神奇。
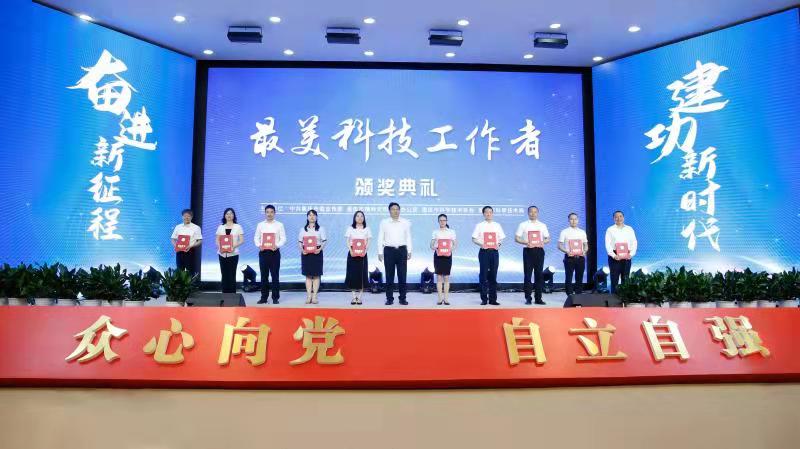

王智彪教授獲2021年重慶市“最美科技工作者”表彰
6月29日上午,為慶祝中國共產黨成立 100 周年,推動重慶市“為科技工作者辦實事助科技工作者作貢獻”行動走深走實,由重慶市科學技術協會舉辦的重慶市科技英才慶建黨百年華誕報告會暨2021 年重慶市“最美科技工作者”表彰大會在重慶科技館舉行。