The key technology introduction and development forecast of the Internet of Things-物聯網關鍵技術的引進及發展的預測

物聯網關鍵技術的引進及發展的預測
The key technology introduction and development forecast of the Internet of Things
Abstract:This paper introduces the background, definition of Internet of Things and the key technologies such as RFID technology, WSN technology of it; From the basic structure of Internet of Things, this paper emphatically analyzes the related concepts and design of RFID middleware and through to the technology of itself and analysis of market combined, I make a forecast and analysis to the future prospects of Internet of Things.
Keywords:Internet of Things; Key technology; Forecast and analysis;
1. IntroductionDue to the technical development of modern micro-electromechanical systems, microelectronics, System on Chip SOC, Nano-materials, sensors, wireless communications, computer networks, distributed information processing, wireless sensor networks (Wireless Sensor Networks, WSN) and radio frequency tags (Radio Frequency Identification RFID ) In recent years, rapid development. These two technologies are independent of each other, but there are inextricably linked, they cross each other and mutual integration, with a very broad application prospects in the military and national defense, industrial and agricultural control, urban management, biomedical, environmental monitoring, emergency many areas have a major disaster relief, counter-terrorism anti-terrorism, hazardous area, remote control, logistics management, personnel identification, automotive research and practical value, has attracted the attention of domestic and international research and industry-wide. When the deepening of the development of these technologies with today's Internet technology, Internet-based expansion and extension to form a new generation of network technology, the Internet of Things was born. The Internet of Things is a development opportunity facing humanity this century, known as the first change human life. Wide range of applications of the Internet of Things will be the information revolution, computers, the Internet and mobile communication network after another.
Technology of Internet of Things has been a widespread concern in recent years. The concept of the "Internet of Things" is on the basis of the "Internet Concepts", which refers to the types of sensors and the Internet interface between new technologies. Its purpose is to make all of the items are connected to the network to facilitate the identification and management involves identifying, sensing, information transfer and processing and other key technologies. There is no doubt that if the "Internet of Things" era, people's daily lives will have seen dramatic changes.
2. Theory of Internet of Things 2.1 Definition of Internet of Things
The Internet of Things is various sensing devices such as radio frequency identification (RFID) device, infrared sensors, global positioning systems, laser scanners and other devices and the Internet combine to form the a huge network. It refers to the types of sensors and the Internet interface in a new technology. Its purpose is to make all of the items are connected to the network to facilitate the identification and management involves identifying, sensing, information transfer and processing and other key technologies.#p#分頁標題#e#
2.2 The key technologies of Internet of Things
In 2005, the ITU published a report entitled "Internet of Things", its first author, Laura, Srivastava said: "We are now standing at the entrance of a new era of communication, in this day and age, we know the Internet will be undergoing a fundamental change in the ITU report of Things There are four key technologies: tag things RFID sensor network technology, perceive things, thinking things smart technology nanotechnology, miniature things.
2.2.1 RFID
RFID (radio frequency identification, radio frequency identification) RFID is a non-contact automatic identification technology, automatic target recognition by the RF signal and access to relevant data, the recognition process without human intervention, can work in a variety of harsh environments. RFID technology can identify the high-speed moving objects can also identify multiple tags, quick and easy operation. RFID technology and the Internet, telecommunications and other technology, can be realized goods tracking and sharing of information worldwide.
Compared with the current widespread use of automatic identification technology such as cameras, bar codes, magnetic cards, IC cards, RFID technology has many outstanding advantages: First, non-contact operation, long-distance identification (a few centimeters to tens of meters), so without human intervention to complete the identification work, the application of convenience; Second, no mechanical wear, long life, and can work in a variety of grease, dust, pollution and other harsh environments; can identify fast moving objects can also identify multiple electronic tags; the reader has a physical interface does not open directly to the end user, to ensure its own security;, data security, except the password protection of electronic tags, data portion can be used a number of algorithms to achieve security management; Sixth, there is a mutual authentication process between the reader and the tag, secure communications and storage.
Currently, RFID technology in industrial automation, object tracking, transport control and management, security and military purposes has been a wide range of applications.
(1) the basic components and how it works
The most basic RFID system consists of the following part of the composition:
① Electronic tags: The coupling components and chips, and each electronic tag has a globally unique identification number cannot be modified, cannot imitate, so to provide security. Electronic tag attached to the object to identify the target object. The electronic tags are normally saved in the agreed format of electronic data, in practical applications, the electronic tag attached to the surface of the object to be recognition.
②Reader: read (or write) the equipment of the electronic tag information can be designed for handheld or fixed.
③Antenna: wireless communication between RFID tags and readers, RF signal space propagation and the establishment of connected devices.#p#分頁標題#e#
④Middleware: a message-oriented, and can accept requests by the application software side, initiate and receive specified one or more readers, the results of data processing returns to the application software specialization software.
⑤Application Software: end-user of RFID applications-oriented interactive interface to help users complete the instruction operation of the reader, as well as middleware logic set, and step by step to RFID atomic events into use can understand the business events, and use visual interface display.
The basic working principle of the RFID technology is not complicated: the label into the magnetic field, receiving the RF signal emitted by the reader, by virtue of the induced current energy to send out product information stored on the chip (passive tags or passive tags), or active to send a frequency signal (active tags or active tags); readers to read and decode the information sent to the central information system for the data processing.
(2) RFID technology standard outlines
RFID technology standards developed by ISO and IEC. Currently available to the RF card of several radio frequency technology standard ISO/IEC10536, ISO / IEC 14443, ISO / IEC 15693 and ISO/IEC18000. The most widely used is the ISO / IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC15693, the two standards are the physical characteristics, radio frequency power and signal interface, initialization and anti-collision and the four components of the transport protocol.
2.2.2 WSN
(1) Introduction of WSN
WSN is a wireless sensor network; short for wireless sensor networks. The sensor network will be able to expand the capacity of people with the real world for remote interaction. Wireless sensor network is a new information access platform, real-time monitoring and collection of a variety of detection of objects in the distribution network within the region, and this information is sent to the gateway node in order to achieve the specified range of target detection and tracking, rapid deployment, anti-survivability characteristics of strong and has a broad application prospects. Business Week and MIT Technology Review reports predict future technological development, wireless sensor networks as the 21st century's most influential 21 technology and change the world, 10 technical one.
(2) WSN network structure
WSN network is usually divided into the physical layer, MAC layer, network layer, transport layer, application layer. The physical layer defines the physical parameters of communication in the WSN, which band, which signal modulation and demodulation. The MAC layer defines the initialization of each node, by sending and receiving beacons, request, and associate the message to complete their own network definitions, and debug strategy of the MAC frame defined at the same time, to avoid communication conflicts between multiple transmitting and receiving nodes. At the network layer to complete the logical routing information collection, send and receive network packages able to follow a different strategy, using the most optimal path to reach the target node. The transport layer provides the reliability of the parcel transfer; provide access to the application layer. The application layer will eventually integrate the collected node information processing, to meet different application needs.#p#分頁標題#e#
2.2.3 Intelligent Technology and Nanotechnology
Smart technology is to achieve some intended purpose to use the knowledge used in a variety of ways and means. Intelligent system implanted in the object, can make objects with a certain intelligence can be active or passive communication with the user, is also one of the key technologies of the Internet of Things.
Nanotechnology is the study of the structure size within the range of 0.1 to 100 nm. Nature of the material and application, the advantages of nanotechnology means that smaller and smaller objects in the Internet of things which can interact and connect. Current trends in electronic technology devices and systems smaller、faster and cooler. More faster means faster response speed; colder refers to the power of a single device. But smaller is not without limits.
3.1 Middleware Profile
Middleware is one of the basic software categories; belong to the scope of reusable software. As the name suggests, the middleware is in the middle of the operating system software with the user's application software.
Middleware in the above operating system, network and database application software lower the overall effect is in the top of the application software to run the development environment to help users with flexible, efficient development and integration of complex applications. IDC expressed in a number of middleware definition more widely accepted: middleware is an independent system software, or services program, distributed application software with this software to share resources between the different technologies, in the middle in client-server operating systems, management of computing resources and network communications.
RFID middleware is to achieve data transmission between the RFID hardware and application systems, filters, an intermediate data format conversion program, a variety of data read by the RFID reader, through the middleware extraction, decryption, filtering, format conversion, import management information systems, program interface for the operator to browse, select, modify, query and response through the application of the system. Middleware technology also reduces the difficulty of application development, developers do not need to directly face the underlying architecture, and make calls through the middleware.
RFID middleware is a message-oriented middleware; information is passed to one or more program modules in the form of a message from a program module. The messages can be asynchronously transmitted; the sender does not have to wait for a response. RFID middleware on the basis of the existing enterprise application middleware development, with its own application features to further expand and deepen the enterprise application middleware in the enterprise. Its main features are:
(1) Independence. RFID middleware independence between the RFID reader and back-end application does not depend on an RFID system and application systems, and can connect with more than one RFID reader and multiple back-end application in order to reduce architecture and its complexity.#p#分頁標題#e#
(2) Data Streams. It is the most important part of the RFID middleware, its main task is the entity object format into the information environment of virtual objects, and data processing is the most important RFID functionality. RFID middleware with data collection, filtering, integration and transmission characteristics, so that the correct object information transmitted to the enterprise back-end application systems.
(3) The processing flow. RFID middleware is a messaging middleware function is to provide a sequence of message flow, data flow design and management capabilities. The need to maintain the data transmission path, data routing and data distribution rules in the system. Data security in data transmission, including the consistency of the data to ensure that the data received by the recipient and sender. But also to ensure the security of data transmission.
3.2 middleware works
Reader continues to receive a series of EPC numbers, of which the most important of the whole process, is also the most difficult part is to deliver and manage these data. EPC numbers of Things network, the Reader will be collected to send to the Middleware, middleware for processing of these data to obtain useful data to the application system. Figure1 shows the RFID system flow chart.
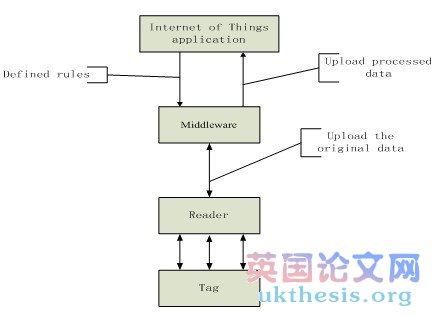
Figure 1 RFID system flow chart
RFID middleware plays an intermediary role between the RFID Reader and applications. Internet of Things applications to specify a rule, the booking of the tag data to the middleware, and applications to the middleware rules maintained by the middleware. Defined in the rule: the reader to inventory data, labeling data reporting cycle start and end conditions, the tag data how to filter tag data contains the raw data.
The application client uses middleware provided by a set of common application programming interface (API) that is able to connect to the RFID reader to read RFID tag data. As a result, even if the RFID tag information is stored database software or back-end applications to increase or change replaced by other software, or other types of read and write RFID reader occurs, the application side need to modify to be able to handle, eliminating the need for many to many connections to maintain the complexity of the problem. RFID middleware is a message-oriented middleware (MOM), the information is in the form of the message, sent from one program to one or more program information can be transmitted in an asynchronous manner, so send does not have to wait for a response. Message-oriented middleware contains features not only the transmission of information, interpret the data must also include security, data broadcasting, error recovery, locating network resources, find out the cost of the path, message priorities and requirements as well as an extension of the debugging tools and other services.
4. Things Industry wide range of applicationsThe Internet of Things is an extension of the Internet is an important part of the new generation of IT. Interconnection between objects and the Internet of Things, with a comprehensive sense, reliable transmission, intelligent processing features, so that mankind can use more refined and dynamic management of production and living, thereby increasing the information capacity of the community as a whole.#p#分頁標題#e#
Internet of Things refers to things and things of interconnection between networks and applications, are widely used in such fields as transportation, logistics , security, electricity, home, divided into three parts of the perception layer, network layer and application layer, sensing layer including a variety of perceived devices and terminal equipment, sensing devices, including RFID tags, two-dimensional code, a variety of sensors , cameras and other network layer is divided into two parts of the access, transport, application layer, including a variety of application services platform. The more mature applications such as smart logistics, smart transportation, smart grid, security monitoring, smart card system.
Industry chain from the point of view, the hardware responsible for the production of all levels of hardware devices, such as the perception of the devices、 terminal equipment、network hardware and servers etc. Software companies responsible for various aspects of software development, data collection, transmission, storage, processing and display functions. System integrators through the combination of hardware and software structures, networking systems, and delivery service providers, Internet of things to achieve the specific application. China's Internet of Things in the early stages of development, systems integration companies generally have both software development and provide services directly to customers, hardware companies are relatively independent.
5. Countries to support industrial development of The Internet of ThingsIn 2009, The Internet of Things gradually was supported by the Governments. The world's major countries have to develop networking as an important means to get rid of the financial crisis, economic recovery and occupation of the commanding heights of global competition. The United States "Smarter Planet Plan, the EU will also be the Internet of things rose to the regional strategic height. Industrial system of global Internet of Things is currently being established and perfected, is expected in 2015, the global Internet of Things the market will reach $ 330 billion, an annual growth rate will reach 25%. The Internet of Things in China industry output will reach 750 billion Yuan, more than 30 percent compound annual growth rate.
The Internet of Things in our country is a closed loop applications, the industry is more dispersed, the lack of uniform standards of Things industry in the State of Things on the basis of strategic planning, China has successively established national standards groups, working groups and the Internet of Things research and development center . In May 2011, the Ministry of Industry and the Ministry of Finance issued on do 2011 things networking development funds, the project application notice made ??it clear that in 2011 the development of things special funds will focus on support of Things key core technologies and key products R & D and industrialization, to support the demonstration and promotion of the key areas of application. Issued by the local governments such as Shanghai, Shanghai propellant networking industry development program of action (2009-2012), focusing on support for intelligent transportation, logistics management, and intelligent security sub-industry.#p#分頁標題#e#
6 .Summary and OutlookITU 2005 report had portrayed the picture of the era of the "Internet of Things": car when the driver operational errors will automatically alarm; briefcase will remind the owner forgot something; clothes will "tell" the washing machine on the color and water temperature requirements and so on. There is no doubt that if the "Internet of Things" era, people's daily lives will have seen dramatic changes.
In fact, the network visible in real life applications, such as a remote anti-theft, intelligent library, but these are only the prototype of the Internet of Things, has not yet formed a huge network. Internet of Things of course build a very good blueprint, but the current global situation to the development of things facing many problems, such as the Internet of Things, you must first memory bank to embed electronic tags on all items, and need to install a number of read equipment and a huge amount of information processing system, which will inevitably lead to a lot of capital investment. The items attached storage will lead to the rise in cost of goods, cost has not yet dropped to the popularity of the premise, the development of the Internet of Things will be limited.
7. References[1]CHENG Man, WANG Rang-hui(School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044,China);Advance in Technical Research and Application of Internet of Things[J];Geomatics World;2010-05
[2]HONG Hai-liang, JIN Jie(Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072,China);Investigation of platform of the Internet of things based on the telecom operates[J];Telecom Engineering Techniques and Standardization;2011-04
[3]LAN Jie(China University Of Mining And Technology, Xuzhou 221000,China);Discussion on the Internet of Things[J];Computer Knowledge and Technology;2011-04
[4]LIU Kai-hua,LI Xiong(Information Occupation Technique Institute of Hunan, Changsha 410001,China);The Status of Internet of Things Application and Opportunity of Evolution[J];Computer Knowledge and Technology;2011-05
[5]Cai Fuqiang1,Guo Bing1,Shen Yan2 (1.Department of Computer Science, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065,China;2.University of Electronic Science and Technology);External Program Loading Function for μC/OS-Ⅱ[J];Microcontrollers & Embedded Systems;2010-09
[6]CAO Feng,ZHANG Minming,LIU Deming, DENG Lei, IAN Yinbo(1.College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering,Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074,China; 2.Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan 430074,China);Design of Network Video Surveillance System Used in the Internet of Things[J];Video Engineering;2011-01
[7]Future Development Outlook for Internet of Things[J];Information Technology & Standardization;2010-04
[8]Xing Rongxin (Calibration and Test Center of China Electronic Standardization Institute, Beijing 100176);RFID tag tester calibration[J];Electronic Measurement Technology;2011-03#p#分頁標題#e#
[9]Huang Gang Lei Xiaoyan(Taiyuan Institute of Technology Taiyuan, Shanxi 030008,China);Ultra low power consumption design of electronic tag[J];Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument;2010-10
[10] Jin Zhao 、Zhuang Yiqi、Qiao Liping 、Liu Weifeng、 Xiao Lei(1.Key Laboratory of Wide Band-Gap Semiconductor Materials and Devices,Xidian University, Xi’an 710071,China; 2.School of Information Technology, Tibet Institute for Nationalities,Xianyang 712082,China);RFID low-power baseband processor according with the link timing[J];Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument;2011-04
[11] Steven. Jeruf,The Internet of Things from RFID to the Next-Generation Per vasitive Networked Systems,AUERBACH Press,2009.
[12] International Telecommunication Union UIT.ITU Inter-net Reports 2005: The Internet of Things[R].2005.
[13] AKYILDIZ L F,et al. Wireless sensor networks:A survey[J].Computer Networks,2002,38:393-422.
