留學生dissertation方法論Methodology寫作范例參考

02-12, 2017
印度銀行業的企業管治常規:方法論
Corporate governance practices in the banking sector of India - Methodology
本章概述了本研究采用的研究方法。第4.1節介紹了研究的背景。4.2節研究目標概述,其次是在第4.3節數據收集和方法。第4.4節包括假設制定和在第4.5節所提出的模型包括。
企業組織雖然形式多樣,結構多樣,已經存在了許多世紀了。這些不同形式的組織產生的主要目的,要么是財富的產生,要么是社會的服務。根據公司組織的最新形式,在已過去的三個世紀流行是自由企業制度。
Chapter 4 – Research Methodology
This chapter outlines the research methodology adopted in this study. Section 4.1 describes the background of the research. The research objectives are outlined in the Section 4.2, followed by data collection and methods in Section 4.3. Section 4.4 includes hypothesis formulated and the proposed model is included in Section 4.5.
4.1 Background of the Research
Corporate organizations though in different forms and structures, have been in existence for many centuries now. The main aim for which each of these different forms of organizations came into being was either wealth generation or service to the society. According to Shah (2008) the most recent form of corporate organizations, which has been in vogue for the last three centuries is the free enterprise system.
Post, Preston & Sachs (2002) state that, the modern corporation is the centre of a network of interdependent interests & constituents for which each are contributing for its performance & each anticipating benefits as a result of the organization’s activities. Once as early as 1946, Peter Drucker says that the core image of the corporation is that the corporate formed is socially created and not a natural phenomenon, which means that the broad social norms and values need to be an inherent requirement for the corporate system as a whole.
To incorporate & abide by the social norms and values “Corporate Governance” emerged as a buzzword in the era of globalization. Organizations are incorporating and are putting a sharper focus on the ethical practices for the benefit of their performance & the benefit of society as a whole.
The fundamental concern of corporate governance is to ensure the means by which a firm’s managers are held accountable to capital providers for the use of assets. The responsibilities and functions of the corporate board in both developed & developing nations are receiving greater attention as a result of the increasing recognition that a firm’s corporate governance affects both its economic performance and its ability to access patient, low-cost capital. The past five years has witnessed a proliferation of corporate governance guidelines & codes of “best practice” designed to improve the ability of corporate directors to hold managements accountable.#p#分頁標題#e#
The extent to which the banks actually practice the professed corporate governance norms is still a moot question. Banks are a critical component of any economy. The importance of banks to national economies is underscored by the fact that banking is virtually universally a regulated industry & that banks have access to government safety nets. It is of crucial importance, therefore, that banks have strong corporate governance. Unlike, the rest of the corporate world, authorities like RBI and the government play a direct role in the bank governance through bank regulation & supervision. This role is justified by the need to ensure systematic stability, financial stability & deposit insurance liability considerations.
Need for good governance in the banking sector is very important because banks play crucial role, banks act as custodian of money and have government dominance. A substantial chunk of Indian Banking sector still remains under the control of public sector banks despite the entry of some private banks in the arena. The public banks are new to the concept of corporate governance (Bansal, 2005).
In the modern era many organizations are making “ethical failures”. It is also important to understand why companies follow good corporate governance practices. Different companies have different motives. Diwedi (2010) opines that one set of companies follow it because it is just a legal obligation; Second set of companies do it because of the pressure of globalization – these are the companies who have the intentions to do business abroad. For them it helps a trust among the foreign stakeholders that they are dealing with a company sound in transparency & ethical standards; The third motive is to show an image of a good corporate citizen so that your stakeholders trust you more and the most crucial fourth reason is of the companies, who believe that the following good governance practices is good for them and such companies go beyond the letter of the law & practice corporate governance in its true spirit.
In the era of globalization & so many corporate failures there is a need for more of these fourth type of companies to lift the overall standards of corporate governance in the country. So, there is a need to revise the old corporate model to build a stronger corporate foundational base. Prof. Subhash Sharma (2010) suggested a need of a new ‘Tripod Model’ based on the inter-linkages & integration of market, society & self. He said that in this framework Market, Society & Self will be considered as “Co-creators of Wealth with grace”. This model can also lead us towards a new performance scorecard on the basis of Holistic Performance of the corporation. The old corporate model which was there to maximize the return to shareholders fails on its ethical foundations. Corporations tend to ignore importance of social discourse on justice & the importance of higher self. This is leading to many failures.#p#分頁標題#e#
Character competence of the corporation reflects good governance & good ethical practices in business. Prof. Sharma (2007) proposed a Character Competence Index which can be based in corporate governance of the organizations by showing its obligations towards Stakeholders.
So far the literature reviewed on the research theme, it appears that in modern times, the new concern in the corporate world is ‘good governance’. To achieve the expected result in the modern era Stakeholder’s are expecting the corporate to behave in an ethical manner. This implies the need for holistic development. Sharma (2008) suggested a 4 Es model of ‘Holistic development & Management’ and when applied in the corporate context can lead us to the concept of Holistic corporate management. In reference to the model Prof. Sharma says that the Ethics dimension reflects Good Governance & Character Competence of the Corporation.
Earlier the performance of an organization was measured on the basis of its efficiency and financial performance. These ways of performance measurement had their own limitations in terms of Holistic Development of organizations and their social relevance. But, today these aspects have become important for organization’s sustainability. It is envisaged that measuring performance on the basis of ‘Character Competence of the Organizations’ will pave a way in this direction. Through this research work, an attempt is made and a model is designed.
4.2 Research Objectives
The main objective of this study is to determine the corporate governance practices in the banking sector of India. The study targets to identify the practices in different CG issues e.g. level of commitment to good corporate governance, effective board practices, control environment and processes, information disclosure and transparency, shareholders rights, and external monitoring etc. The present study also critically examines the governance prevailing in the banking sector in India. More specifically, the objectives of the study are:
To study the conceptual foundation of Character Competence of the organizations.
To develop measures & indicators of Character Competence for the Indian Banking Industry.
To study the relationship between Character Competence, Corporate Governance, Stakeholder Relationship and Organizational Performance of the Indian Banking Industry.
To assess the gap between the Ideal character competence & present stage of character competence.
To study the ways to fill the gap between the current & desired Character Competence in the Indian Banking Industry.
4.3 Data Collection and Methods
The primary data collection method used for this research was through structured questionnaire. This study utilized questionnaire and obtained relevant data in a way to achieve research objectives. Questionnaire used in the study consist of four parts with likert scale questions. All the questions included in the questionnaire have been framed from literature review with justification of its validity and reliability. The questionnaire comprises 4 sections: Stakeholder’s Relationship, Corporate Governance, Character Competence and Organizational Performance.#p#分頁標題#e#
The secondary data used for the research was through published data such as Journals, research articles, relevant websites, books and annual reports of Banks.
This study provides a comprehensive comparative analysis of corporate governance regulatory systems in selected banks of India. The main reason of selection of these banks is that their scripts dominate and influence the stock movement of the country. Further, banks considered for the Bankex represents the major banks of the country. Indian banking sector comprises the varieties of banks that can be divided as Public Sector Banks, Private Sector Banks, Foreign Banks and Co-operative Banks etc. Though, corporate governance bind to all type of banks but for precise focus, researcher has selected the banking companies listed in the BANKEX [BSE]. The banks are divided in three groups: Public Sector Banks, Private Sector Banks and Foreign Banks.
The list of Group III banks which is shown in the above table contains names of foreign banks, which contains total 3 banks. Out of the total sample size, banks from the foreign banks are 13.63%. The list is arranged alphabetically.
The questionnaire survey was undertaken in four cities Delhi, Mumbai, Lucknow and Kanpur and the target of this survey were top and middle level managers from different Public, Private and Foreign Banks.
The information about the top and middle level managers included their name, designation and email address and was collected in person and through email by the researcher. 250 respondents answered to the questionnaire. Respondents were requested to rate their degree of agreement against each of the identified statements according to a five-point Likert scale (1 = Strongly Disagree and 5 = Strongly Agree). The obtained raw data were inputted and analyzed with the aid of the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) computer software. Prior to the implementation of the research, a pilot study was conducted. Respondents were prompted to answer the preliminary questionnaire. The aim of the pilot study was to pre-test the suitability and validity of the questionnaire. Pilot study was conducted on the sample size of 40. There were no adverse comments proposed, so the finalized questionnaire is the same as that of the first version.
The data collected through the pilot study was tested under factor analysis. A factor analysis was used to determine the underlying relationships among the 55 statements. It also attempts to identify trustfulness of the survey and its underlying variables that explains the pattern of correlation within a set of observed variables (Frederick & Larry, 2008). The principal component analysis for factor extraction was applied to categorize the factors into a fewer number of groupings. Validating and refining of all the 55 critical factors is important for data analysis, reliability and validity tests of the raw data were conducted depending on the overall data and results of factor analysis.#p#分頁標題#e#
For the strength of relationship among the factors, the correlation matrix (Tabachnik and Fidell 1996) was conducted. The data collected under the study was tested under Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability Testing. A Cronbach’s Alpha is the most common measure of internal consistency (“reliability”). It is the most common used when you have multiple likert questions in a questionnaire that form a scale, and you wish to determine if the scale is reliable and finally the testing of the hypothesis.
4.4 Hypothesis:
Some of the Indicative Hypothesis for my Research was:
Ho: There is no impact of Character Competence on Corporate Governance.
Ha: There is an impact of Character Competence on Corporate Governance.
Ho: There is no impact of Character Competence on Stakeholder’s Relationship.
Ha: There is an impact of Character Competence on Stakeholder’s Relationship.
Ho: There is no impact of Corporate Governance on Stakeholder’s Relationship.
Ha: There is an impact of Corporate Governance on Stakeholder’s Relationship.
Ho: There is no impact of Character Competence on Organizational Performance.
Ha: There is an impact of Character Competence on Organizational Performance.
Ho: There is no impact of Corporate Governance on Organizational Performance.
Ha: There is an impact of Corporate Governance on Organizational Performance.
Ho: There is no impact of Stakeholder’s Relationship on Organizational Performance.
Ha: There is an impact of Stakeholder’s Relationship on Organizational Performance.
Ho: There is no impact of combined effect of Character Competence, Corporate Governance and Stakeholder’s Relationship on Organizational Performance.
Ha: There is an impact of combined effect of Character Competence, Corporate Governance and Stakeholder’s Relationship on Organizational Performance.
4.5 Proposed Model:
From the above concerning Literature Review, there is some relationship between Character Competence of an organization, Corporate Governance and Stakeholder’s Relationship. Combining the three may have some effect on the Organizational Performance. The relationship between these can be depicted as below:
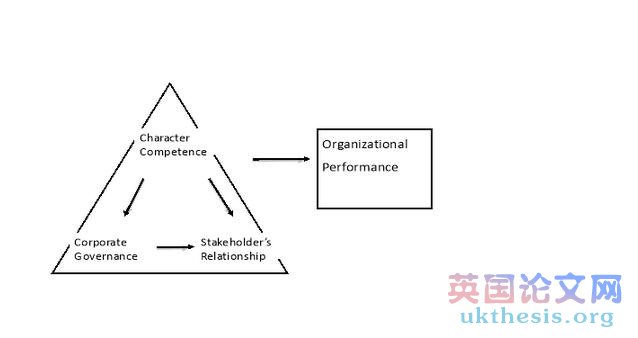
Figure 4.1: Proposed Model
The above diagrammatic representation can be conceptualized as there is impact of Character Competence on Corporate Governance and Stakeholder’s Relationship. Corporate Governance has an impact on Stakeholder’s Relationship. If all the three constitute they have an impact on Organizational Performance.#p#分頁標題#e#
